What is the FAIRtracks tool assembly?
The FAIRtracks ecosystem is a set of services associated with a minimal metadata model for genomic annotations/tracks, implemented as a set of JSON Schemas. The FAIRtracks model contains metadata fields particularly useful for data discovery, harmonised through strict adherence to a selection of ontologies available through the Ontology Lookup Service. The usability of the model can be expanded through referencing the original records via Compact Uniform Resource Identifiers (CURIEs) resolvable by Identifiers.org.
In the context of the Data Life Cycle and its stages, the FAIRtracks ecosystem covers Collecting, Processing, Analysing, Sharing, and Reusing. It has to be noted, however, that the FAIRtracks ecosystem is structured around a secondary data life cycle, as illustrated in Figure 1. As part of this secondary life cycle, the annotation/track data gets further distributed and its discovery is enhanced through derived metadata. The FAIRtracks ecosystem aims at harmonising this process. Primary data needs to be handled independently following domain best practices (see e.g. the pages on Single cell sequencing, Plant sciences, or Rare disease data).
The FAIRtracks ecosystem is developed and provided as part of the national Service Delivery Plans by ELIXIR Norway and ELIXIR Spain, and is supported by the Track Hub Registry group at EMBL-EBI. FAIRtracks is endorsed by ELIXIR Europe as a Recommended Interoperability Resource.
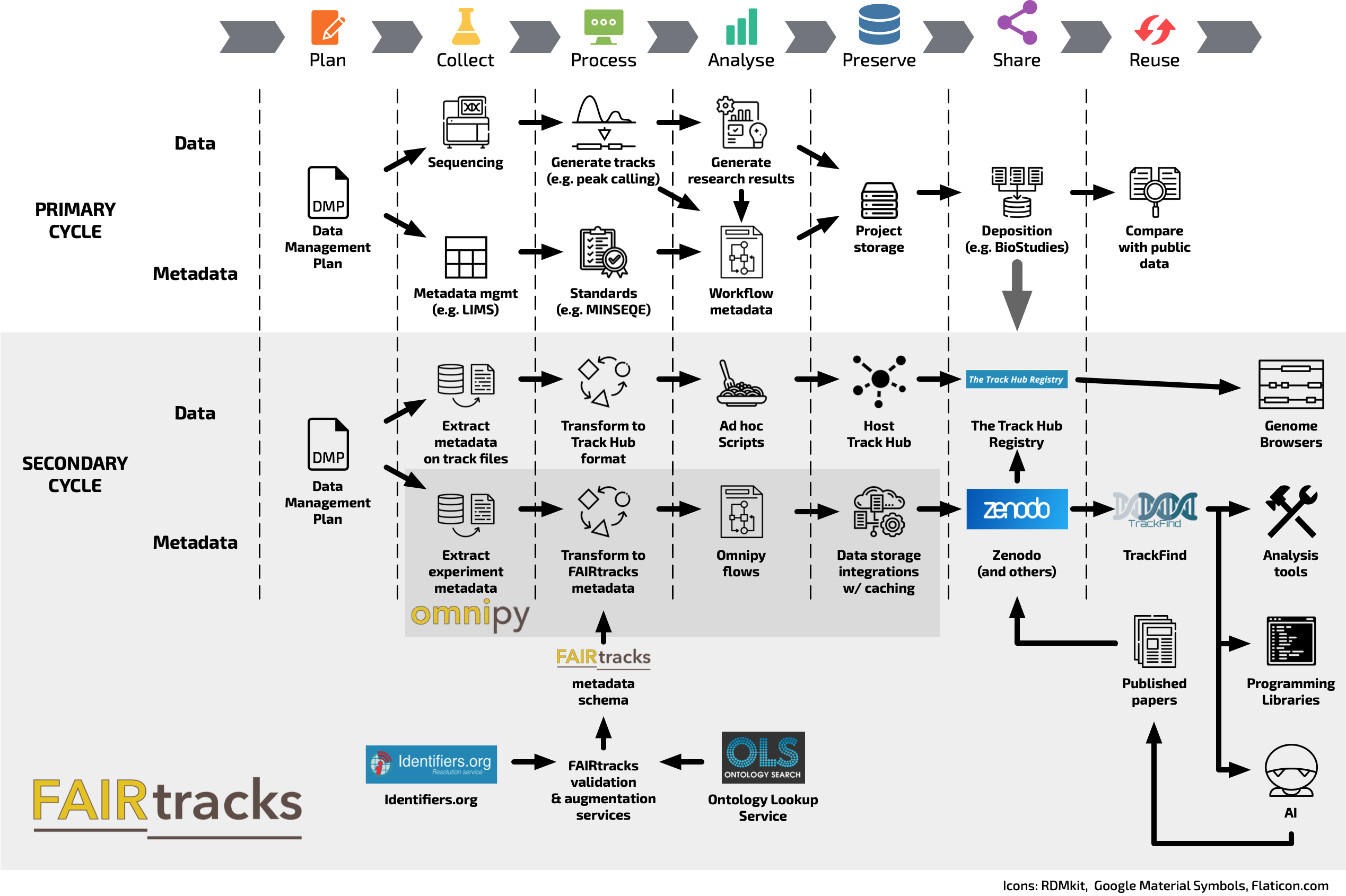
Figure 1. Illustration of the Data life cycle for the FAIRtracks tool assembly. As genomic tracks/annotations often represent condensed summaries of the raw data, this ecosystem covers a secondary cycle designed around the FAIRtracks metadata model. The grey box shows the areas of relevance for the FAIRtracks ecosystem with its integrations, and only a subset of the icons represents FAIRtracks services per se. Omnipy (dark grey box) is a general Python library for scalable and reproducible data wrangling which can be used across several data models and research disciplines.
Who can use the FAIRtracks tool assembly?
There is no central authentication solution for the FAIRtracks services requiring login. The entire FAIRtracks ecosystem is available to everyone. Most of the services are accessible through Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). More details are provided in the description below. Users of the FAIRtracks ecosystem belong to different categories, which could be summarised as:
- Researchers and data analysts
- Data providers and biocurators
- Developers working on tooling for
- Research
- Implementation of the FAIR data principles
Each of these categories benefits specifically from a subset of the global ecosystem. The core services can be accessed both upstream (for data providers and biocurators) and downstream (for tool developers and analytical end users).
For what can you use the FAIRtracks tool assembly?
The FAIRtracks tool assembly can be used for a large number of applications; we summarise the main ones below following the steps of the data life-cycle and focusing on particular tools.
While the assembly does not include a tool for Data Management Planning, the FAIRtracks metadata standard is registered in FAIRsharing and, thus, formally connected to several other standards and databases. The FAIRtracks standard can, thus, be selected on your Data Management Plan in all the instances of Data Stewardship Wizard through the integration with FAIRsharing.
Omnipy is a high-level Python library for type-driven data wrangling and scalable data flow orchestration; it is a self-standing subset of the FAIRtracks ecosystem covering several steps in the data life-cicle. It can be used to extract metadata from specific portals and for Processing of metadata entries to harmonise them into a unique model. Omnipy data flows are defined as transformations from specific input data models to specific output data models. Input and output data are validated at each iteration through parsing based on Pydantic. Offloading of data flows to external compute resources is provided through the integration of Omnipy with an orchestration engine based on Prefect.
There is ongoing work into adding Prefect as one of the services available in the National Infrastructure for Research Data (NIRD) service platform. This would enable running Omnipy on data and metadata stored in the NIRD data storage. Refer also to the Norwegian national page for more details. Note that, while the usage of NIRD storage and services is certainly convenient for Norwegian users, this is not a central or mandatory part of the tool assembly which is born as an international service and aims at maintaining this status.
Data Sharing and preservation is one of the key components of the FAIRtracks ecosystem. Since genomic annotations/tracks typically consist of secondary data files referring to primary data sources, they are often deposited together with the primary data. The aim of the minimal metadata model is to offer a greater level of granularity, providing each track with an identifier and enabling the possibility of analysis across datasets in an automatised fashion. A dedicated registry would typically be required to accomplish this. Given that such a registry does not yet exist, the current recommendation is to deposit FAIRtracks-compliant metadata files to Zenodo, as this platform supports both Digital Object Identifier (DOI) versioning and DOI reservation before publication. The identifiers on the metadata FAIRtracks object are then cross-linked with the actual data which is hosted e.g. in a Track Hub and registered in the Track Hub Registry.
Data and metadata organised in this fashion can be discovered for Reusing through TrackFind, a search and curation engine for genomic tracks. TrackFind will import FAIRtracks-compliant metadata from e.g. Zenodo. This metadata can be accessed through hierarchical browsing or by search queries both through a web-based user interface and as a RESTful API. TrackFind supports advanced SQL-based queries that can be easily built into the user interface.
Additional tools that comprise the core of the FAIRtracks ecosystem are the metadata validation and the metadata augmentation services. The former is REST API that extends the standard JSON Schema validation technology to e.g. validate ontology terms or check CURIEs against the registered entries. The FAIRtracks augmentation service is implemented as a REST API that expands on the information contained in a minimal FAIRtracks JSON by adding a set of fields with human-readable values including ontology labels, versions, and summaries. This service bridges the gap between data providers, which are required to submit only minimal information, and data consumers who require richer information for data discovery and retrieval.
Related pages
More information
Training
Skip tool tableTools and resources on this page
| Tool or resource | Description | Related pages | Registry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Stewardship Wizard | Publicly available online tool for composing smart data management plans
|
CSC Plant Genomics Plant Phenomics Plant sciences Data management plan GDPR compliance | Tool info Training |
| FAIRsharing | A curated, informative and educational resource on data and metadata standards, inter-related to databases and data policies. | Health data Microbial biotechnology Plant sciences Virology Data discoverability Data provenance Data publication Existing data Machine actionability Documentation and meta... | Standards/Databases Training |
| Identifiers.org | The Identifiers.org Resolution Service provides consistent access to life science data using Compact Identifiers. Compact Identifiers consist of an assigned unique prefix and a local provider designated accession number (prefix:accession). | Identifiers | Tool info Standards/Databases Training |
| Omnipy | Omnipy is a high level Python library for type-driven data wrangling and scalable workflow orchestration. | Tool info Training | |
| Ontology Lookup Service | EMBL-EBI's web portal for finding ontologies | Bioimaging data Enzymology and biocata... Health data Documentation and meta... | Tool info Standards/Databases Training |
| Prefect | Prefect is a workflow orchestration tool empowering developers to build, observe, and react to data pipelines. | ||
| Pydantic | Pydantic is the most widely used data validation library for Python. | Training | |
| Track Hub Registry | A global centralised collection of publicly accessible track hubs | Standards/Databases | |
| TrackFind | TrackFind is a search and curation engine for metadata of geneomic tracks. It supports crawling of the TrackHub Registry and other portals. | Tool info | |
| Zenodo | Generalist research data repository built and developed by OpenAIRE and CERN | Plant Phenomics Bioimaging data Biomolecular simulatio... Enzymology and biocata... Plant sciences Single-cell sequencing Data publication Identifiers | Standards/Databases Training |
National resources
Tools and resources tailored to users in different countries.
| Tool or resource | Description | Related pages | Registry |
|---|---|---|---|
| NIRD | The National Infrastructure for Research Data (NIRD) infrastructure offers storage services, archiving services, and processing capacity for computing on the stored data. It offers services and capacities to any scientific discipline that requires access to advanced, large-scale, or high-end resources for storing, processing, publishing research data or searching digital databases and collections. This service is owned and operated by Sigma2 NRIS, which is a joint collaboration between UiO, UiB, NTNU, UiT, and UNINETT Sigma2. |
Data transfer Data storage NeLS |

